Service Registration
Introduction
The Bloonix WebGUI provides an API that allows services to be automatically registered and removed when necessary. Each service is always assigned to a specific host. Each host, in turn, has its own unique host ID. This ensures a clear service-to-host mapping and allows service discovery processes to be flexibly adapted. In addition, services can be individually configured using variables.
Setup in the WebGUI
To create a new configuration for service registration, navigate through the menus as shown in the following screenshot:
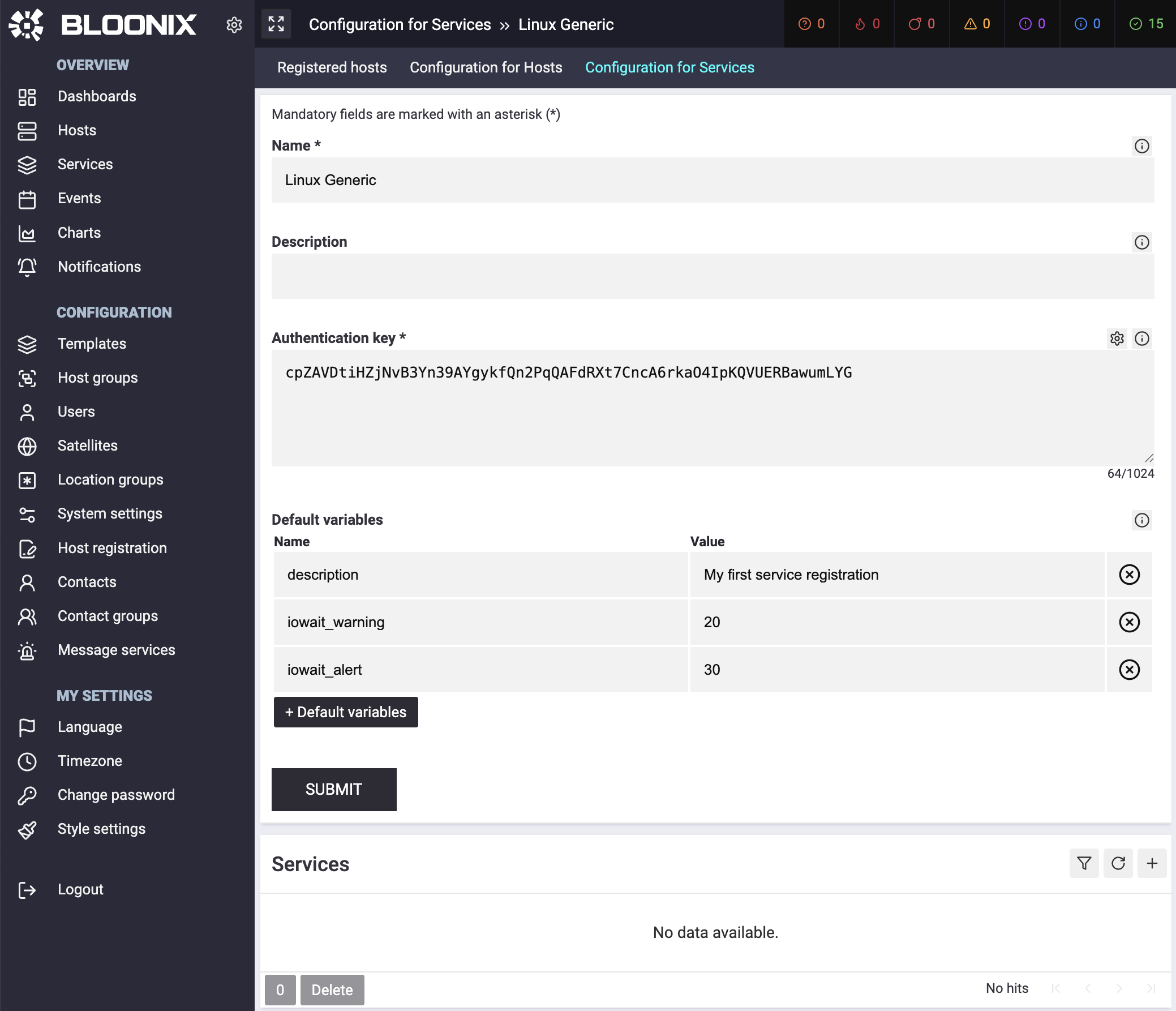
After submitting the form, additional configuration options will appear. Here you can define the services that should be registered via the API:
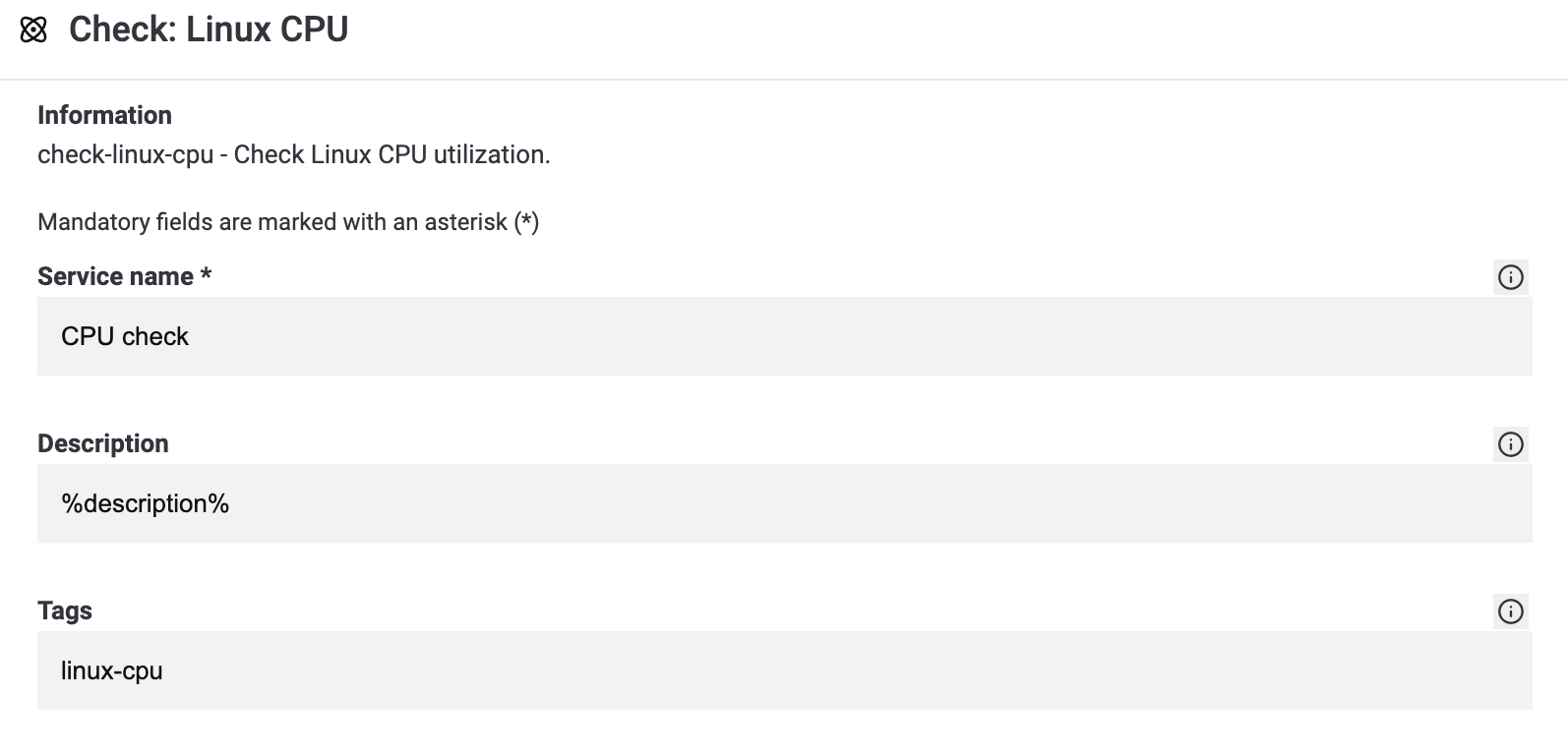
Now let’s move on to setting up the services. It is important that each service is assigned a tag. This tag is required for the registration of the service. The following screenshots show an example of setting a tag and the variables description and iowait_alert.

To configure a service for a host, you can use a simple cURL command. Example:
curl -XPOST https://webgui.example/register/service -d '
{
"host_id": 12345,
"password": "password",
"authkey": "authkey",
"tag": "linux-generic",
"variables": {
"description": "Overwrite the default variable",
"iowait_alert": 50
}
}The following happens:
- The service is copied from the registration configuration.
- The variables description and iowait_alert are overridden.
- The variable iowait_warning is not defined and will be taken from the default variables.
- The service is directly assigned to the specified host ID.
Note that variables that are not defined will not be replaced. The placeholders will be copied. These should at least be set in the host variables; otherwise, errors may occur during check execution.
Removing Services
Services created through the registration process can also be removed the same way. The prerequisite is that object removal is enabled in the system options. Important: When creating the service, an object ID must be assigned, as removal can only be done using this ID. If a service does not have an object ID, it cannot be deleted via the API.
In the following example, we create a service with a fixed object ID:
curl -XPOST https://webgui.example/register/service -d '
{
"host_id": 12345,
"password": "password",
"authkey": "authkey",
"tag": "linux-generic",
"object_id": "linux-cpu",
"variables": {
"description": "Overwrite the default variable",
"iowait_alert": 50
}
}'To remove this service later, a simple cURL command with the object ID is sufficient:
curl -XPOST https://webgui.example/register/service/delete-object-id -d '
{
"host_id": 12345,
"password": "password",
"object_id": "linux-cpu"
}'If multiple services share the same object ID, they will all be removed together. This can happen, for example, during the deprovisioning of Docker containers for which multiple services with the same object ID (container name) were created during provisioning.